Difference between revisions of "XinuPhone"
| (15 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | XinuPhone is an innovative hardware/software platform for Internet telephony education and research. In the classroom, XinuPhone promotes hands-on interactive learning that is both cross-discipline and application oriented. As a research tool, XinuPhone is a versatile and open-source platform useful for benchmarking experimental methods against industry standards. Furthermore, the XinuPhone platform features inexpensive commodity hardware that is easy to assemble making it an idea choice for users on | + | XinuPhone is an innovative hardware/software platform for Internet telephony education and research. In the classroom, XinuPhone promotes hands-on interactive learning that is both cross-discipline and application oriented. As a research tool, XinuPhone is a versatile and open-source platform useful for benchmarking experimental methods against industry standards. Furthermore, the XinuPhone platform features inexpensive commodity hardware that is easy to assemble making it an idea choice for users on tight budgets and in diverse educational backgrounds. |
[[File:xinuphone-system.jpg|1000px]] | [[File:xinuphone-system.jpg|1000px]] | ||
| − | == | + | ==How It Works== |
| + | Most of the Embedded Xinu [[List_of_supported_platforms|supported platforms]] do not have the ability to directly [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nyquist%E2%80%93Shannon_sampling_theorem sample analog signals] or [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Digital-to-analog_converter reconstruct analog waveforms] from digital bitstreams. Likewise, typical digital signal processing (DSP) chips lack Ethernet networking hardware and protocol support. XinuPhone pairs a simple external sampling module with a network-enabled backend running the Embedded Xinu operating system in order to provide both functionalities. | ||
| − | + | The XinuPhone audio module consists of filters, a digital signal controller (DSC), an audio amplifier, and a serial transceiver. Speech first passes through an analog low-pass anti-aliasing filter before it enters the analog to digital converter (ADC) on the DSC. The DSC can be programed with a variety of software [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Codec CODECs] that compress the sampled audio for efficient transmission across the serial bus. The serial transceiver allows the audio module to interface directly with an RS-232 capable network device, such as a slightly modified Linksys WRT54GL router. The audio module sends serial samples to the network device; then, the Embedded Xinu operating system [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Voice_over_IP VoIP] tools packetize the serial data and send the voice packets to a remote host. On the receiving end, another network device buffers incoming packets and translates the payloads back into a stream of serial data. The external audio module uses the same CODECs to uncompress the serial data back into raw audio samples. Lastly, a digital to analog converter (DAC) on-board the DSC converts the audio samples back to an analog waveform that can be amplified and played back. | |
| − | == | + | == Hardware == |
| + | You can build your own XinuPhone with readily available discrete components! | ||
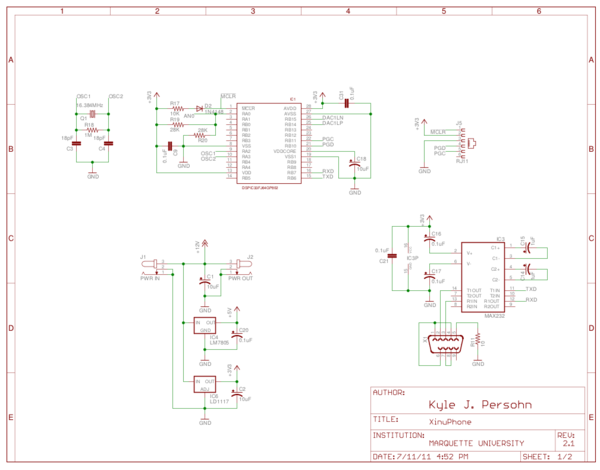
| − | == | + | === Schematics === |
| + | [[File:Xinuphone-schematic-page1.png|600px]] | ||
| − | ==External Links== | + | Sheet 1 shows the basic DSC core, power supply, crystal oscillator, debug interface, and serial transceiver connections. |
| − | ===Microchip=== | + | |
| + | |||
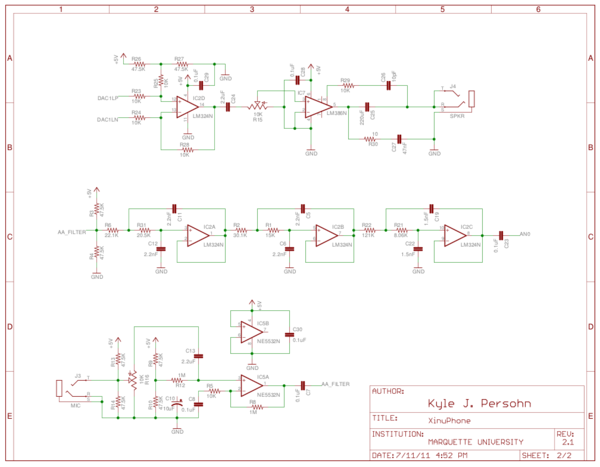
| + | [[File:Xinuphone-schematic-page2.png|600px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Sheet 2 illustrates the headphone amplifier, microphone pre-amplifier, and low-pass anti-aliasing filter. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Click on the sheet for a higher resolution image or see the downloads below for a PDF rendering. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Design Notes === | ||
| + | * Components are specified to EIA E96 standard values for resistors (1% tolerance) and E24 values for capacitors. | ||
| + | * For capacitors in the audio path, temperature coefficient X7R, NP0, C0G, or better are recommended. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Downloads == | ||
| + | {|cellpadding="2" | ||
| + | ! File | ||
| + | ! Download Link | ||
| + | ! Checksum (SHA1) | ||
| + | |-style="background-color: #fdfdfd" | ||
| + | | rowspan="2" | XinuPhone Firmware 1.0 (Binary+Source) | ||
| + | | style="text-align:center" | [http://www.mscs.mu.edu/~kpersohn/xinuphone/download/xinuphone-1.0.tar.gz gzip] | ||
| + | | 8aa4b4d7ed38c4c641e920905aabfee1a9d2dbc0 | ||
| + | |-style="background-color: #fdfdfd" | ||
| + | | style="text-align:center" | [http://www.mscs.mu.edu/~kpersohn/xinuphone/download/xinuphone-1.0.tar.bz2 bzip2] | ||
| + | | 6ecfecbb9d9bc399b961d0764923ce609b4c569a | ||
| + | |-style="background-color: #fdfdfd" | ||
| + | | XinuPhone Hardware Schematic Rev 2.1 | ||
| + | | style="text-align:center" | [http://www.mscs.mu.edu/~kpersohn/xinuphone/xinuphone.pdf pdf] | ||
| + | | a0f07d543f2b85440c31daa7d530066f682a8a5a | ||
| + | |-style="background-color: #fdfdfd" | ||
| + | | Embedded Xinu Operating System | ||
| + | | style="text-align:center" | [http://xinu.mscs.mu.edu/Downloads url] | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Instructional Resources == | ||
| + | * Interactive Real-Time Embedded Systems Education Infused with Applied Internet Telephony. Kyle Persohn, Dennis Brylow. COMPSAC 2011: Proceedings of 35th IEEE Computer Software and Applications Conference, pages 199-204, Munich, Germany, July 2011. [http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/COMPSAC.2011.33 link] | ||
| + | * [[Teaching With Xinu]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Future Work == | ||
| + | * Real-Time Transport Protocol support in Embedded Xinu | ||
| + | * Analog Telephone Adapter (ATA) interface | ||
| + | * Simple XinuPhone discovery protocol / address book | ||
| + | |||
| + | == External Links == | ||
| + | Some additional resources you may find useful | ||
| + | ==== Microchip ==== | ||
* [http://www.microchip.com/wwwproducts/Devices.aspx?dDocName=en532310 dsPIC33FJ64GP802 Product Home] | * [http://www.microchip.com/wwwproducts/Devices.aspx?dDocName=en532310 dsPIC33FJ64GP802 Product Home] | ||
* [http://www.microchip.com/stellent/idcplg?IdcService=SS_GET_PAGE&nodeId=1406&dDocName=en019469&part=SW007002 MPLAB IDE] | * [http://www.microchip.com/stellent/idcplg?IdcService=SS_GET_PAGE&nodeId=1406&dDocName=en019469&part=SW007002 MPLAB IDE] | ||
* [http://www.microchip.com/stellent/idcplg?IdcService=SS_GET_PAGE&nodeId=2660¶m=en535144 Audio & Speech Application Libraries] | * [http://www.microchip.com/stellent/idcplg?IdcService=SS_GET_PAGE&nodeId=2660¶m=en535144 Audio & Speech Application Libraries] | ||
| − | ===Standards & RFCs=== | + | ==== Standards & RFCs ==== |
* [http://www.itu.int/net/itu-t/sigdb/genaudio/Pseries.htm ITU-T Test Signals for Telecommunication Systems] | * [http://www.itu.int/net/itu-t/sigdb/genaudio/Pseries.htm ITU-T Test Signals for Telecommunication Systems] | ||
* [http://www.itu.int/rec/T-REC-G.711/en ITU-T G.711 - Pulse Code Modulation (PCM) of Voice Frequencies] | * [http://www.itu.int/rec/T-REC-G.711/en ITU-T G.711 - Pulse Code Modulation (PCM) of Voice Frequencies] | ||
* [http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc3550.txt RFC 3550 - RTP: A Transport Protocol for Real-Time Applications] | * [http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc3550.txt RFC 3550 - RTP: A Transport Protocol for Real-Time Applications] | ||
| − | ===PCB Fabrication=== | + | ==== PCB Fabrication ==== |
* [http://www.4pcb.com Advanced Circuits] | * [http://www.4pcb.com Advanced Circuits] | ||
* [http://www.cadsoftusa.com/ CadSoft EAGLE Schematic Capture & Board Layout Software] | * [http://www.cadsoftusa.com/ CadSoft EAGLE Schematic Capture & Board Layout Software] | ||
* [http://www.sparkfun.com/tutorials SparkFun Tutorials] | * [http://www.sparkfun.com/tutorials SparkFun Tutorials] | ||
Latest revision as of 23:32, 5 June 2012
XinuPhone is an innovative hardware/software platform for Internet telephony education and research. In the classroom, XinuPhone promotes hands-on interactive learning that is both cross-discipline and application oriented. As a research tool, XinuPhone is a versatile and open-source platform useful for benchmarking experimental methods against industry standards. Furthermore, the XinuPhone platform features inexpensive commodity hardware that is easy to assemble making it an idea choice for users on tight budgets and in diverse educational backgrounds.
Contents
How It Works
Most of the Embedded Xinu supported platforms do not have the ability to directly sample analog signals or reconstruct analog waveforms from digital bitstreams. Likewise, typical digital signal processing (DSP) chips lack Ethernet networking hardware and protocol support. XinuPhone pairs a simple external sampling module with a network-enabled backend running the Embedded Xinu operating system in order to provide both functionalities.
The XinuPhone audio module consists of filters, a digital signal controller (DSC), an audio amplifier, and a serial transceiver. Speech first passes through an analog low-pass anti-aliasing filter before it enters the analog to digital converter (ADC) on the DSC. The DSC can be programed with a variety of software CODECs that compress the sampled audio for efficient transmission across the serial bus. The serial transceiver allows the audio module to interface directly with an RS-232 capable network device, such as a slightly modified Linksys WRT54GL router. The audio module sends serial samples to the network device; then, the Embedded Xinu operating system VoIP tools packetize the serial data and send the voice packets to a remote host. On the receiving end, another network device buffers incoming packets and translates the payloads back into a stream of serial data. The external audio module uses the same CODECs to uncompress the serial data back into raw audio samples. Lastly, a digital to analog converter (DAC) on-board the DSC converts the audio samples back to an analog waveform that can be amplified and played back.
Hardware
You can build your own XinuPhone with readily available discrete components!
Schematics
Sheet 1 shows the basic DSC core, power supply, crystal oscillator, debug interface, and serial transceiver connections.
Sheet 2 illustrates the headphone amplifier, microphone pre-amplifier, and low-pass anti-aliasing filter.
Click on the sheet for a higher resolution image or see the downloads below for a PDF rendering.
Design Notes
- Components are specified to EIA E96 standard values for resistors (1% tolerance) and E24 values for capacitors.
- For capacitors in the audio path, temperature coefficient X7R, NP0, C0G, or better are recommended.
Downloads
| File | Download Link | Checksum (SHA1) |
|---|---|---|
| XinuPhone Firmware 1.0 (Binary+Source) | gzip | 8aa4b4d7ed38c4c641e920905aabfee1a9d2dbc0 |
| bzip2 | 6ecfecbb9d9bc399b961d0764923ce609b4c569a | |
| XinuPhone Hardware Schematic Rev 2.1 | a0f07d543f2b85440c31daa7d530066f682a8a5a | |
| Embedded Xinu Operating System | url |
Instructional Resources
- Interactive Real-Time Embedded Systems Education Infused with Applied Internet Telephony. Kyle Persohn, Dennis Brylow. COMPSAC 2011: Proceedings of 35th IEEE Computer Software and Applications Conference, pages 199-204, Munich, Germany, July 2011. link
- Teaching With Xinu
Future Work
- Real-Time Transport Protocol support in Embedded Xinu
- Analog Telephone Adapter (ATA) interface
- Simple XinuPhone discovery protocol / address book
External Links
Some additional resources you may find useful
Microchip
Standards & RFCs
- ITU-T Test Signals for Telecommunication Systems
- ITU-T G.711 - Pulse Code Modulation (PCM) of Voice Frequencies
- RFC 3550 - RTP: A Transport Protocol for Real-Time Applications