Difference between revisions of "TTY Driver"
| (8 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
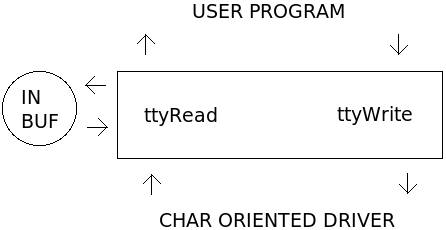
| − | [[Image: | + | [[Image:TtyDriver.png|right|450px]]The TTY driver serves as an intermediary device between hardware device drivers and user applications to provide line buffering of input and cooking of input and output. The driver is purely software oriented and makes no direct communication with physical hardware. Instead, the TTY driver relies on an underlying device driver to communicate directly with the hardware. The [[Shell|XINU Shell]] utilizes a TTY device to line buffer and cook user input read from the [[UART_Driver|UART]]. |
| − | == | + | == Open & Close == |
| − | + | Open associates a TTY with an underlying char-oriented hardware device. The underlying device driver must provide both getc and putc functions for the TTY to obtain input and send output character by character. The device should already be opened and initialized before the TTY is opened. When a TTY is opened, its device control block, input buffer, and flags are initialized. No input flags are set when a TTY device is opened. The TTY_ONLCR output flag is set when a TTY device is opened. | |
| − | + | Close disassociates a TTY from its underlying device and resets the TTY's device control block. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | == | + | == Read == |
| − | + | The TTY driver reads characters from an underlying device driver using the devices getc function. Input is first buffered in the TTY driver's circular buffer before being copied to the user buffer supplied as a parameter in the <code>ttyRead</code> function call. | |
| − | + | The <code>ttyRead</code> function begins by checking the <code>ieof</code> flag to determine if the EOF character (Control+D) was read during the last call to <code>ttyRead</code> If the <code>ieof</code> flag is set, the function returns the <code>EOF</code> constant, defined in <code>stddef.h</code>. <code>EOF</code> is only returned once for each EOF character read by the TTY driver. A call made to <code>ttyRead</code> after <code>EOF</code> was returned, will result in an attempt to read more characters from the underlying device driver. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | If the <code>TTY_IRAW</code> flag is set, the TTY driver performs no line buffering or line editing (input cooking). The user buffer is first filled from any data remaining in the TTY driver's input buffer from the last <code>ttyRead</code> call. The remaining portion of the user supplied buffer is filled by reading characters from the underlying device driver. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | The TTY driver performs line buffering and line editing (input cooking) when the <code>TTY_IRAW</code> flag is not set. Characters are read from the underlying device driver until a line delimiter is read or the TTY driver's input buffer is full. Lines may be terminated with the newline (LF or <code>'\n'</code>) or end of file (EOF or ASCII character 0x04) characters. If the <code>TTY_ECHO</code> flag is set, each character is output as it is read. | |
| − | + | Special handling is required for some characters to perform line editing (input cooking). If the TTY driver's input buffer contains characters, backspace (BS or <code>'\b'</code>) and delete (DEL or ASCII character 0x7F) remove the last character from the TTY's input buffer. The newline and carriage return (CR or <code>'\r'</code>) characters are cooked if certain input flags are set. The end of file character causes the <code>ieof</code> flag to be set. Any other unprintable characters are ignored. | |
| − | '' | + | After a line of input is buffered in the TTY's device driver, the user supplied buffer is filled from the TTY's input buffer. If the end of file character was the only character read, the <code>EOF</code> constant is returned. Otherwise, the number of characters read into the user buffer is returned. |
| − | + | The TTY driver has the following input flags: | |
| − | + | * <code>TTY_IRAW</code> - reads input unbuffered and uncooked | |
| + | * <code>TTY_INLCR</code> - converts '\n' to '\r' | ||
| + | * <code>TTY_IGNCR</code> - ignores '\r' | ||
| + | * <code>TTY_ICRNL</code> - converts '\r' to '\n' | ||
| + | * <code>TTY_ECHO</code> - echoes input | ||
| − | '' | + | == Write == |
| + | The TTY driver does not buffer output; it writes characters directly to an underlying device driver. The TTY driver cooks newlines (LF or <code>'\n'</code>) and carriage returns (CR or <code>'\r'</code>) if certain output flags are set. | ||
| − | + | The TTY driver has the following output flags: | |
| − | + | * <code>TTY_ONLCR</code> - converts '\n' to '\r\n' | |
| − | + | * <code>TTY_OCRNL</code> - converts '\r' to '\n' | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | == Control == | |
| + | The TTY driver has four control functions: two to set and clear input flags and two to set and clear output flags. Each of control functions returns the previous state of the flags being changed. | ||
== See also == | == See also == | ||
* [[UART Driver]] | * [[UART Driver]] | ||
Latest revision as of 19:58, 23 May 2008
The TTY driver serves as an intermediary device between hardware device drivers and user applications to provide line buffering of input and cooking of input and output. The driver is purely software oriented and makes no direct communication with physical hardware. Instead, the TTY driver relies on an underlying device driver to communicate directly with the hardware. The XINU Shell utilizes a TTY device to line buffer and cook user input read from the UART.
Contents
Open & Close
Open associates a TTY with an underlying char-oriented hardware device. The underlying device driver must provide both getc and putc functions for the TTY to obtain input and send output character by character. The device should already be opened and initialized before the TTY is opened. When a TTY is opened, its device control block, input buffer, and flags are initialized. No input flags are set when a TTY device is opened. The TTY_ONLCR output flag is set when a TTY device is opened.
Close disassociates a TTY from its underlying device and resets the TTY's device control block.
Read
The TTY driver reads characters from an underlying device driver using the devices getc function. Input is first buffered in the TTY driver's circular buffer before being copied to the user buffer supplied as a parameter in the ttyRead function call.
The ttyRead function begins by checking the ieof flag to determine if the EOF character (Control+D) was read during the last call to ttyRead If the ieof flag is set, the function returns the EOF constant, defined in stddef.h. EOF is only returned once for each EOF character read by the TTY driver. A call made to ttyRead after EOF was returned, will result in an attempt to read more characters from the underlying device driver.
If the TTY_IRAW flag is set, the TTY driver performs no line buffering or line editing (input cooking). The user buffer is first filled from any data remaining in the TTY driver's input buffer from the last ttyRead call. The remaining portion of the user supplied buffer is filled by reading characters from the underlying device driver.
The TTY driver performs line buffering and line editing (input cooking) when the TTY_IRAW flag is not set. Characters are read from the underlying device driver until a line delimiter is read or the TTY driver's input buffer is full. Lines may be terminated with the newline (LF or '\n') or end of file (EOF or ASCII character 0x04) characters. If the TTY_ECHO flag is set, each character is output as it is read.
Special handling is required for some characters to perform line editing (input cooking). If the TTY driver's input buffer contains characters, backspace (BS or '\b') and delete (DEL or ASCII character 0x7F) remove the last character from the TTY's input buffer. The newline and carriage return (CR or '\r') characters are cooked if certain input flags are set. The end of file character causes the ieof flag to be set. Any other unprintable characters are ignored.
After a line of input is buffered in the TTY's device driver, the user supplied buffer is filled from the TTY's input buffer. If the end of file character was the only character read, the EOF constant is returned. Otherwise, the number of characters read into the user buffer is returned.
The TTY driver has the following input flags:
TTY_IRAW- reads input unbuffered and uncookedTTY_INLCR- converts '\n' to '\r'TTY_IGNCR- ignores '\r'TTY_ICRNL- converts '\r' to '\n'TTY_ECHO- echoes input
Write
The TTY driver does not buffer output; it writes characters directly to an underlying device driver. The TTY driver cooks newlines (LF or '\n') and carriage returns (CR or '\r') if certain output flags are set.
The TTY driver has the following output flags:
TTY_ONLCR- converts '\n' to '\r\n'TTY_OCRNL- converts '\r' to '\n'
Control
The TTY driver has four control functions: two to set and clear input flags and two to set and clear output flags. Each of control functions returns the previous state of the flags being changed.